Election Denial in Oregon
0 Election Deniers currently hold statewide office with election oversight power.
8 Election Deniers have held, or run for, statewide office since 2020.
1 Election Denier are sitting members of Congress.
0 Election Deniers hold statewide Office right now.
Elections are run by the states. In Oregon, the Governor, Attorney General, and Secretary of State are the state officials responsible for overseeing elections. It’s up to them to make sure the will of the people is always respected.
Read more about The Roles of Our Elected Officials in Elections
No candidates match the selected filters.
1 Election Denier is sitting members of congress right now.
Election Deniers make up 13 percent of Oregon’s 8-member Congressional delegation. Members of Congress have a public platform to build up or tear down trust in our elections. And they have concrete responsibilities, too, such as determining federal funding for elections.
Read more about The Roles of Our Elected Officials in Elections

Representative of Oregon, District 2
Term started 2025
Term ends 2027
-
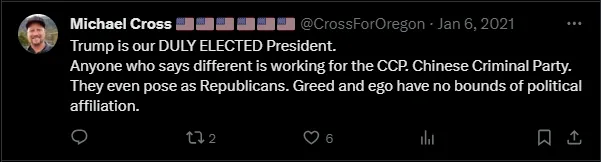
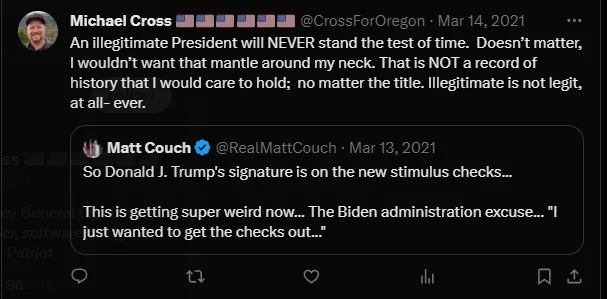
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
How Oregon compares
Every state runs its own elections, with its own laws and processes. Check out how Oregon compares with other states in its region when it comes to Election Deniers holding state election administration jobs.
Election Denial in Far West States
| Lieutenant Governor | Moreinformation about Alaska | ||||||
| Moreinformation about California | |||||||
| State Elections Board | Moreinformation about Hawai‘i | ||||||
| Moreinformation about Nevada | |||||||
| Moreinformation about Oregon | |||||||
| Moreinformation about Washington |
Sitting official is an Election Denier
- In Alaska, the chief election official is the Lieutenant Governor, elected alongside the Governor.
- In Hawai'i, the Chief Election Official is appointed by the Hawai'i Elections Commission.
8 Election Deniers have held, or have run for, statewide Office since 2020.
Even one Election Denier with election oversight power is a threat to the will of the people. Here are the Election Deniers who have sought control over Oregon elections in recent years.

Running for Governor of Oregon
-
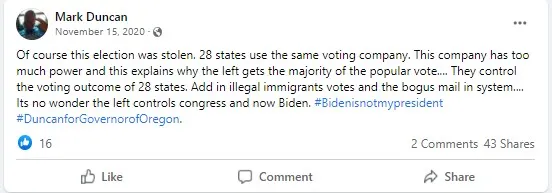
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.

Ran for Governor of Oregon in 2022
-
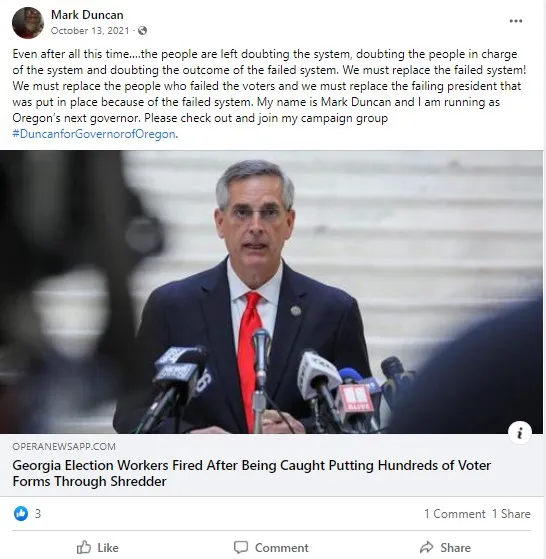
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.

Ran for Governor of Oregon in 2022
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.

Ran for Secretary of State of Oregon in 2024
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
Ran for Governor of Oregon in 2022
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.

Ran for Governor of Oregon in 2022
-
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.

Ran for Attorney General of Oregon in 2024
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.

Ran for Governor of Oregon in 2022
-
Falsely claimed former President Trump won the 2020 presidential election instead of the legitimate winner, President Biden.
-
Spread lies or promoted conspiracies about the legitimacy of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles in public, including in social media, press statements, or comments to the press.
-
Refused to certify, or called on or pressured election officials to refuse to certify, the 2020 presidential election results or a race in subsequent elections based on meritless claims about election fraud, voter fraud, misinformation, or lies.
-
Taken action to undermine the integrity of the 2020 presidential election or subsequent election cycles, including:
Filing or supporting litigation seeking to overturn the results based on conspiracies or baseless legal theories.
Filing or supporting litigation that was sanctioned for being malicious or without merit in the aftermath of an election.
Promoting or participating in a Stop the Steal–sponsored or branded event or rally during or following the 2020 election.
Calling for a “forensic audit” of the 2020 presidential election or a race in subsequent elections after the results were certified, were officially audited, or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
-
Refused to concede a race, or publicly supported a candidate’s refusal to concede a race, after the results were officially audited or stood up to multiple legal challenges.
Voter turnout over time
Voters are always the backstop against election denial, whether Election Deniers are already in office or vying for power. It’s important to turn out for every election in your state—and to vote in every race on your ballot. Downballot races, like contests for Attorney General and Secretary of State, have historically drawn fewer voters, even though the positions are critical to keeping elections free, fair, and secure. Here’s a look at voter participation in Oregon elections over time. Notice that in years with several important positions up for election, some voters choose not to vote in every race.
Voter Participation in Oregon Since 2016
- #071B40
- President
- #2455A0
- Senator
- #4387F1
- Governor
- #A7C5F3
- Attorney General
- #EDF3FD
- Secretary of State
2016 Presidential
-
President had a 69% voter turnout rate
-
Senator had a 67% voter turnout rate
-
Governor had a 67% voter turnout rate
-
Attorney General had a 63% voter turnout rate
-
Secretary of State had a 65% voter turnout rate
-
2018 Midterm
-
Governor had a 62% voter turnout rate
-
2020 Presidential
-
President had a 76% voter turnout rate
-
Senator had a 75% voter turnout rate
-
Secretary of State had a 73% voter turnout rate
-
2022 Midterm
-
Senator had a 61% voter turnout rate
-
Governor had a 62% voter turnout rate
-
Voter turnout
Data on the number of votes cast in each race are from state elections depositories, supplemented with data from the U.S. Election Assistance Commission (EAC), House Election Statistics, and The Book of States. Rates are calculated using the Census’s Citizen Voting Age Population (CVAP) estimates.
Beyond the ballot box
Each year, state legislators introduce thousands of bills related to elections. And in the past few years, we’ve identified a concerning trend. Across the country, state legislatures are considering bills that would make it easier for partisan actors to manipulate an election, and maybe even overturn the will of the people. We’re tracking these bills along with our partners in an ongoing series of reports called “A Democracy Crisis in the Making.” All told, in the 2023 legislative cycle, we identified 196 bills that were introduced in 39 states that would interfere with election administration. Ultimately, 21 of those bills became law across 15 states, while 7 bills were vetoed across 2 states.
The anti-democracy playbook is simple: change the rules and change the referees, in order to change the results. These bills go hand-in-hand with the Election Denier movement: They’re about taking power away from voters and making it harder for trusted election officials to do their jobs.
Legislative Interference in Oregon by Category
As of November 15, 2023, 3 bills had been introduced or were under consideration in Oregon. None have been enacted or adopted and none have been vetoed after passing.
These bills show that the threat to elections in Oregon, and all across the country, goes well beyond the ballot box.
- Imposing disproportionate criminal or other penalties.These bills would create or expand penalties for election officials in the ordinary execution of their jobs, including criminalizing inadvertent mistakes.
- Creating unworkable burdens in election administration.These bills would interfere with the basic procedures of election administration, increasing the risk of chaos and delay and enabling misleading claims of irregularity.
- Requiring partisan or unprofessional election “audits” or reviews.These bills would establish vague post-election review schemes without the professional standards of traditional audits.
- Usurping control over election results.These bills would give legislators or other state officials direct control over election outcomes.
- Seizing power over election responsibilities.These bills would shift election administration responsibilities away from professional, nonpartisan officials and toward partisan actors in the legislature.